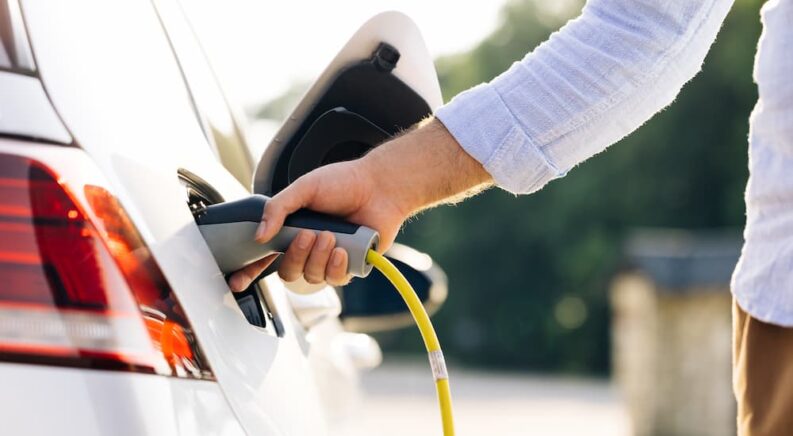
From their unprecedented horsepower and lighting-fast acceleration to their eco-friendly design and low operating costs, there are plenty of good reasons to opt for an electric vehicle when it comes time to buy your next car, truck, or SUV. The EV segment has come a long way in recent years in terms of convenience and price, with growing infrastructure and lucrative tax incentives making all-electric vehicles a more practical option for the average driver. That said, there is still one aspect of the EV lifestyle that can throw some drivers for a loop. Public charging options are more prevalent than ever, but unlocking your EV’s true potential starts with installing a reliable home charging system.
An EV charging system offers unmatched convenience for EV drivers, drastically lowering your charging rates and even increasing the value of your home. A good home charging setup is a must-have for any EV driver, but the installation process can be a little intimidating for those who are more accustomed to thinking about gallons than kilowatt-hours when trying to top off their fuel. Luckily, CheckEngine is here to help with a brief guide to car charger installation issues. Join us as we walk you through some of the dos and don’ts of the installation process and learn just how easy it can be to embrace the EV approach.
Installing the Wrong Charger
Modern EV chargers are divided into three categories: Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3 Charging, also known as DC Fast Charging (DCFC). There are a few important differences between each option, but it largely comes down to an issue of how fast they can top off your battery. A standard Level 1 charger operating at 1.0 to 1.4 kW can bring your EV to 100 percent in between 30 and 40 hours, while a quicker Level 2 charger can complete the process in less than five hours. Level 3 DCFC is the speediest option, with the ability to fully recharge a battery in under an hour, but this isn’t available for home use due to its cost and power requirements.
Why would a driver choose a Level 1 charger when a Level 2 system is so much quicker? It’s largely a matter of installation cost. A Level 1 charger operates on a standard 120-volt connection. In contrast, a Level 2 charger requires a more powerful 240-volt outlet, which means drivers might need to upgrade their home’s electrical system or install a specialized outlet before plugging in. There’s also the matter of the equipment itself. Almost all EVs come with a Level 1 charger right out of the box, but installing a Level 2 system requires an additional investment that can add anywhere from $1,000 to $3,500 to the bottom line.
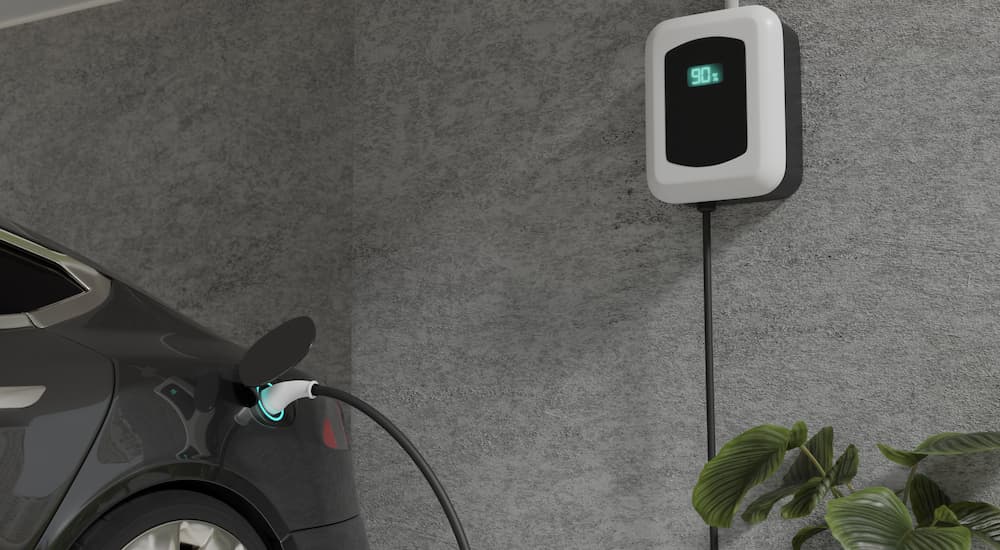

Inadequate Electrical Infrastructure
A Level 2 EV charger requires a 240-volt connection that can put some additional stress on your home’s electric system. Older buildings might be unable to handle the extra load. They may be prone to blowing circuits or even causing electrical fires if tasked with accommodating a Level 2 charger. Your home’s electrical panel, also known as a breaker box, might need to be upgraded with a new circuit breaker or wiring to make room for an EV charger if it’s already at maximum capacity. A qualified electrician can perform a load estimate to determine if upgrades are necessary and help to give you a better idea of what sort of costs might be involved.
There’s also the matter of the outlets. Most homes are already equipped with 240-volt outlets, which power some of the larger appliances we use in everyday life. Clothes dryers, water heaters, electric stoves, and central air conditioning systems tend to run on 240-volt power, but adding an EV charger to the mix might force drivers to add a new outlet. This might be a relatively easy task if your garage is already outfitted with a 240-volt connection, but it could require a little extra work if you’re lacking in outlets.
Ignoring the Professionals
We’re all about the DIY approach, and we always encourage drivers to get their hands dirty and learn a new skill that’ll allow them to be the master of their own vehicle repair and maintenance routine. Unfortunately, that can-do spirit vanishes the moment that higher voltages get involved. Messing around with a 120- or 240-volt electrical connection without the proper training, certification, and tools is a surefire recipe for tragedy. We recommend calling in the pros when it comes time to install a Level 2 EV charger.
A certified electrician specializing in EV charger installation can ensure the system is installed safely and adheres to any regulatory requirements. From avoiding power surges and properly grounding the charger to maximizing charging efficiency and preventing you from running afoul of your charger’s warranty requirements, there’s no substitute for the professional touch. They can also provide helpful advice on where to install the charger, outline a long-term maintenance plan that’ll keep the charger working at its best for years to come, and alert you to any rebates or tax credits that could lower the cost of the installation process.
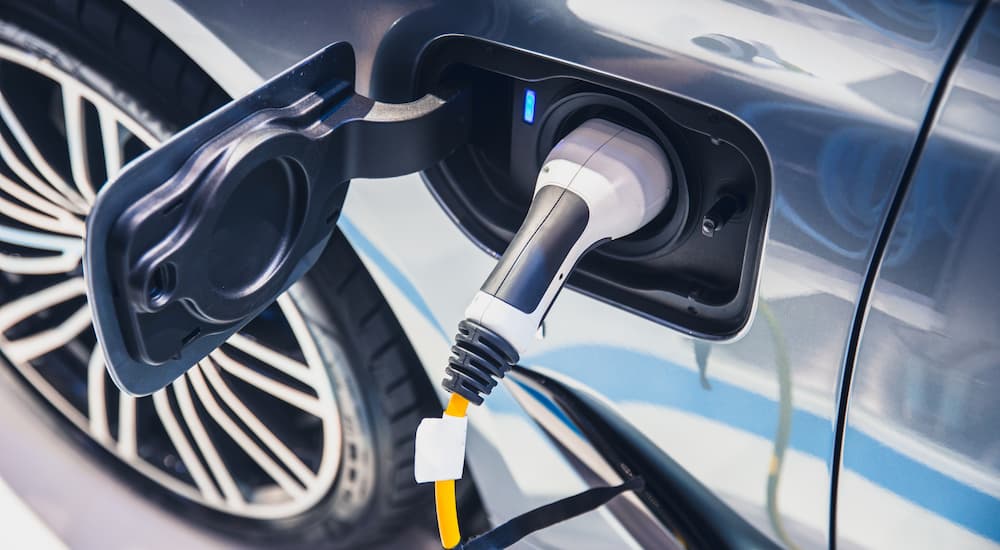

Poor Charger Maintenance
While we’ve covered some of the basic issues around EV charger installation, it’s important to remember that you’ll need to perform a little ongoing maintenance if you expect your setup to last for the long haul. A neglected charger will not only provide subpar performance but could even potentially damage your EV’s electrical system or jeopardize the battery, which is the vehicle’s most expensive component. Drivers should regularly inspect the charger for any signs of damage, including loose connections, damaged plugs, and compromised cables.
One study estimates that around 28 percent of charger failures can be tied to damaged cables, but it’s easy to avoid some costly worst-case scenarios by embracing a few simple habits. Routinely driving over your cables, twisting them into tight coils for storage, or letting the end of the cable rest on the ground can easily shorten their lifespan, so take that extra minute and ensure they’re properly stored when not in use. You’ll also want to inspect the charging ports and connectors for corrosion and keep the charger free of any dust or debris that might find its way into the system’s sensitive electronic components.
You’ve Got the Power
That covers some of the most relevant troubleshooting tips for EV charger installation, but these aren’t the only things to consider when considering a jump to the all-electric segment. Drivers should also take a moment to think about the best place to install an EV charger. A garage is always a great option as it’ll provide protection from the elements, but it might not be an option for those living in urban environments. Again, a qualified electrician or EV charger installation expert can provide helpful guidance and leverage their experience in the EV realm to set you up for success. Just remember to choose the right charger for the task, consider any electrical upgrades you might need, and locate a qualified professional to help guide you through the