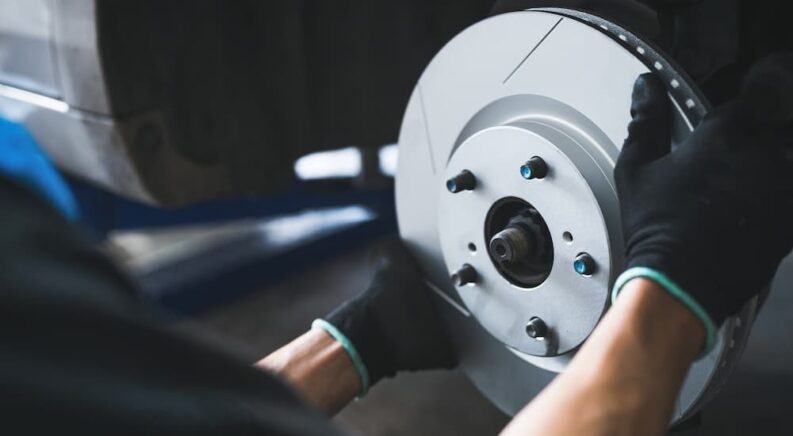
You use the brakes often, even on a short drive, and they must be in good working order. Brake pads are the first thing people think of when it comes to brake maintenance, but many other parts are essential to good stopping performance. The most important part of a disc brake system is the rotors, which play a pivotal role in slowing a vehicle from any speed. The disc-like shape of the rotors is how disc brakes got their name.
Having good rotors on your car can be the difference between a safe stop and a bad accident. This introductory guide has all the basic information that vehicle owners need to know about brake rotors. We’ll go over how they work, how long they typically last, signs that brake rotors need replacement, and everything else to help you keep them in good working order.
What Are Brake Rotors?
Brake rotors are circular components that spin at the same speed as the wheel, passing between the caliper and brake pads without touching under normal conditions. Since disc brakes are predominant in modern vehicles, it is likely yours has rotors. (Older vehicles have drum brakes instead of discs. Some modern budget cars, trucks, and EVs have disc brakes in the front and drum brakes in the rear.)
Pressing on the brake pedal in a disc brake system causes a chain of events that leads to the calipers squeezing the pads against both sides of the rotors, creating friction and resistance. This is what slows and eventually stops the vehicle. The harder you press, the more friction you generate. Along the way, the brake rotors convert the vehicle’s kinetic energy, or motion, into thermal energy, or heat.
Different Types of Brake Rotors
Depending on your needs, there are several brake rotor styles. Modern integral brake rotors fasten to the wheel hub using flanges. On older hat-style rotors, the wheel bearings are part of the rotor, and the assembly goes over the studs onto the spindle.
As for the rotor, the most common design is a solid rotor with a blank, smooth surface, which offers the best functionality and value for everyday driving. Rotors may also be vented in multiple ways. Drilled brake rotors have small holes that allow heat, gas, liquid, and dust to escape. They’re common for performance vehicles where drivers do a lot of high-speed braking. Slotted brake rotors have grooves that clear debris and pad glaze while allowing air to pass through. This makes braking more consistent for trucks and SUVs, though they may not last as long. Drilled and slotted rotors have both holes and grooves, offering the best heat dispersion and debris removal. They offer the best braking performance, but the least durability.
Most rotors are made of high-carbon steel or cast iron, which are affordable and offer good performance and durability. Some high-performance cars have composite ceramic rotors. They have excellent heat dissipation even without drills or slots, and last a lot longer. However, ceramic rotors are much more expensive and don’t handle cold weather well.
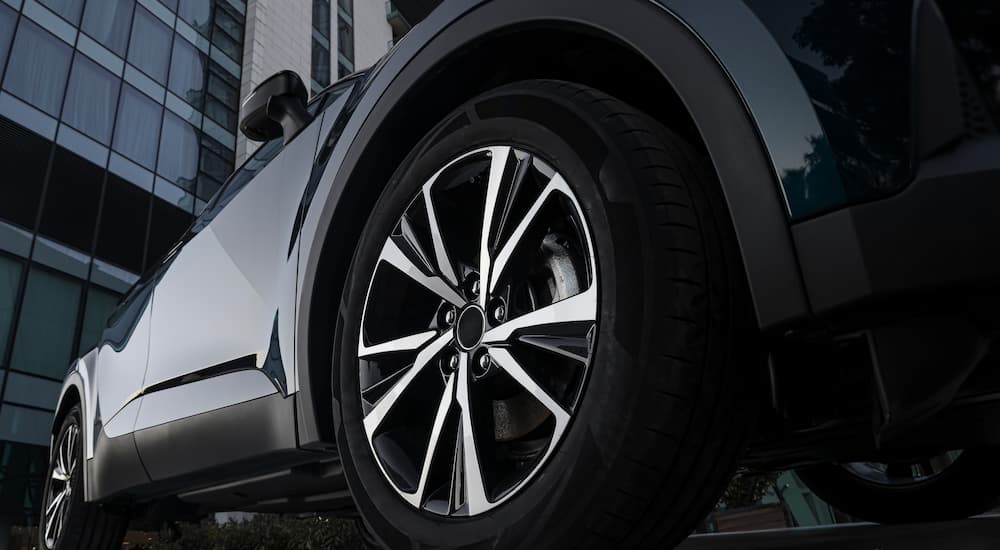

How Long Do Brake Rotors Last?
An OEM set of brake rotors typically lasts between 30,000 and 80,000 miles, though they can go farther in good conditions. Beyond the initial rotor quality, several different factors affect brake rotor lifespan. Doing a lot of stop-and-go city driving, mountain driving, or being more aggressive with your braking (such as “panic stops”) will wear the rotors out faster. Conversely, highway driving is much easier on the rotors, so they last longer. Excessive heat can cause the metal to warp or otherwise become misshapen.
Heavy snow, water, and road salt can lead to rust and corrosion. Driving regularly on dirt roads and trails increases the likelihood of rocks, hard bumps, and other impacts damaging the rotors. Carrying heavy loads and lots of passengers puts more strain on your rotors because you must apply more force to stop the vehicle. Letting the brake pads wear down too far will cause the metal backing plates to scrape against the rotor and damage it.
Regular maintenance, such as cleaning off debris and brake dust or applying a rust prevention product, can get more miles from your rotors. Also, beware that newer vehicles tend to have thinner rotors than older vehicles to reduce weight. The downside of this is that the rotors are not as strong, leaving them more vulnerable to wear and warping.
How Do You Know When to Replace Brake Rotors?
Swapping brake rotors at the first sign of a problem will ensure the best stopping power and safety. If the brake pedal or steering wheel pulses when you apply the brakes, it shows rotor warping or uneven wear. Abnormal brake sounds, like screeching, scraping, and grinding, can also indicate rotor damage. Rotors may show visible signs of damage such as gouges, scratches, heat-discolored areas, or rust. Your vehicle taking longer to stop is a telltale sign of brake system issues, which may include the rotors. If the rotor has a large lip around the edge, it may have worn down too far to be considered safe.
You should inspect and measure your rotors whenever you rotate your tires, swap summer and winter tires, or change your brake pads. Ask an automotive technician to inspect the rotors at your next service appointment if you want a professional opinion.
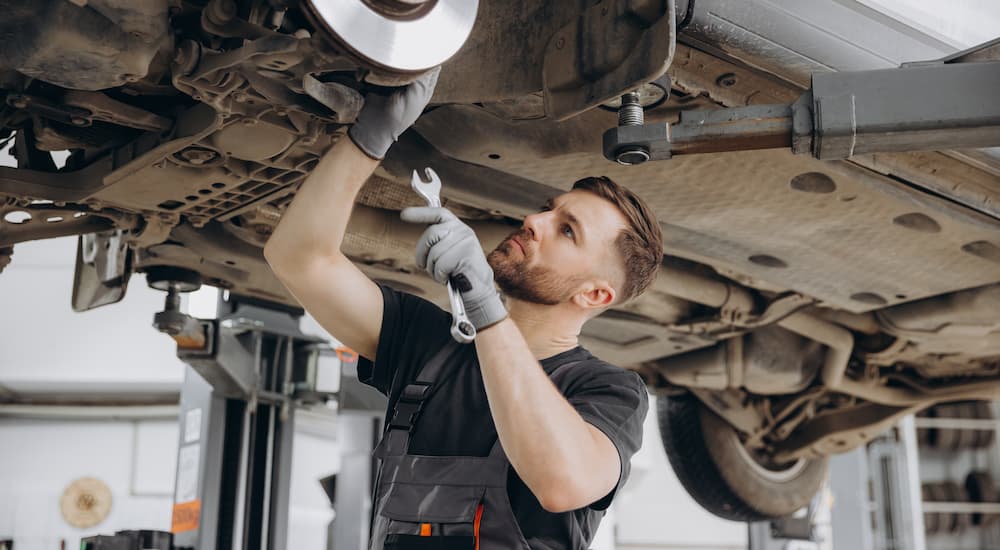

How Much Does Brake Rotor Replacement Cost?
For most everyday vehicles, new brake rotors typically cost between $30 and $80 each. Certified professional installation will add another $150 to $200 per axle. Rotors on performance vehicles, large trucks, and full-size SUVs often cost more because they are larger, contain more material, and require high-end parts and specialized service.
Someone with a reasonable amount of mechanical skill should be able to replace the rotors themselves. The biggest DIY brake rotor replacement tips are to double-check the rotor direction, make sure it’s properly aligned with the hub, and use a torque wrench for the proper bolt tightness. Whether it’s you or a mechanic doing the work, front and rear rotors should be replaced in pairs. If you have a new rotor on the left front but a worn rotor on the right front, it can cause inconsistent braking, pulling to one side, and other issues.
In the case of minor wear and rust, the brake rotor can potentially be resurfaced. This involves putting the rotor on a special lathe to scrape off the uneven top layer and make it smooth again. However, only do this if the resurfaced rotor still meets the minimum thickness recommended by the manufacturer. A rotor that’s too thin will generate more heat, warp more easily, and wear out faster. You also should not resurface a rotor if it has significant warping, large grooves, or any cracks.
Accelerate Your Disc Brake System
Good brakes are not negotiable when it comes to vehicle performance and safety. In addition to your brake pads, calipers, pistons, and fluid, keep a close eye on the brake rotors as part of your maintenance and repair routine. By using the right brake rotors, practicing good driving habits, and replacing the rotors as needed, your brakes will be ready to avert potential disasters. Use the knowledge in this guide to better your understanding of brake rotors, as well as learn about changes and upgrades you can make on a customized vehicle.